Written by Allen Wyatt (last updated December 24, 2024)
This tip applies to Word 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, and 2021
Maren has a document that has a very large table in it, spanning many pages. She would like the ability to jump to a specific row in the table, so she wonders if it is possible to use the Go To feature to jump to a particular row number, such as row 80.
The Go To dialog box (which is displayed by pressing F5 or Ctrl+G) allows you to jump to lots of different places in a document. (How you use the dialog box has been covered in other issues of WordTips.) It is actually possible for it to be used with table rows, with one huge caveat.
If your document only contains a table, you can jump to rows by following these steps:
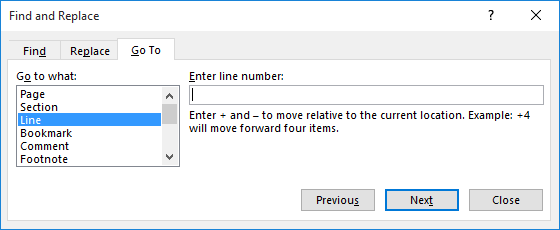
Figure 1. The Go To tab of the Find and Replace dialog box.
This works because Word apparently considers each row in the table a "line." (It isn't affected, either, but rows that contain wrapped lines or multiple paragraphs.) This brings me to the caveat: If your document contains more than a table—especially text before the table—then the line jumping will be off because Word counts the non-table text in its line count calculations.
In that case, you'll need to use a macro to jump to the row you want. The following is an example of one that could be used.
Sub GoToTableRow()
Dim RowNum As Integer
Dim LastRow As Integer
Dim Question As String
If Selection.Information(wdWithInTable) Then
LastRow = Selection.Tables(1).Rows.Count
Question = "Enter a number from 1 to " & LastRow
RowNum = InputBox(Question, 1)
If (RowNum < 1) Or (RowNum > LastRow) Then
MsgBox "That's an invalid row number"
Exit Sub
End If
Selection.Tables(1).Rows(RowNum).Cells(1).Select
Else
MsgBox "Not in table"
End If
End Sub
The macro first checks to make sure the insertion point is within a table. If so, it asks the user which row number he or she would like to jump to. Assuming that the row number is in the range of available row numbers, the row is then jumped to.
Note:
WordTips is your source for cost-effective Microsoft Word training. (Microsoft Word is the most popular word processing software in the world.) This tip (10906) applies to Microsoft Word 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, and 2021.

Discover the Power of Microsoft Office This beginner-friendly guide reveals the expert tips and strategies you need to skyrocket your productivity and use Office 365 like a pro. Mastering software like Word, Excel, and PowerPoint is essential to be more efficient and advance your career. Simple lessons guide you through every step, providing the knowledge you need to get started. Check out Microsoft Office 365 For Beginners today!
Do you need a quick way to format your tables? Believe it or not, there are several tools you can use from Word's arsenal ...
Discover MoreIf you want to have Word highlight rows in a table that contain a certain character, you need to resort to using a macro. ...
Discover MoreFor some programming needs, it is important to determine the index of an object within a collection of such objects. This ...
Discover MoreFREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in WordTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
There are currently no comments for this tip. (Be the first to leave your comment—just use the simple form above!)
Got a version of Word that uses the ribbon interface (Word 2007 or later)? This site is for you! If you use an earlier version of Word, visit our WordTips site focusing on the menu interface.
Visit the WordTips channel on YouTube
FREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in WordTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
Copyright © 2026 Sharon Parq Associates, Inc.
Comments